Tissue Reactions (Deterministic effects) and Stochastic effects
From the biological effects of radiation on human body, radiation effects are generally divided into two categories: "Tissue Reactions (Deterministic effects)" and "Stochastic effects".
Tissue Reactions (Deterministic effects)
Based on a large number of experiments involving animals and other researches, further supplemented by theoretical studies, it was discovered that severity of certain effects on human beings will increase with increasing doses. There exists a certain level, the "threshold", below which the effect will be absent. This kind of effects is called "tissue reactions (deterministic effects)".
Characteristics of tissue reactions (deterministic effects):
- Damage depends on absorbed dose
- Threshold exists
Example: cataract, erythema, infertility etc.
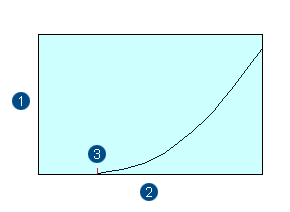
Tissue Reactions (Deterministic effects) and dose relationship
(1) represents severity, (2) represents dose and (3) represents threshold
Severity of tissue reactions(deterministic effects) depends on dose. However, thresholds exist, only above which the effects will occur. In the “Statement on Tissue Reactions (2011)”, International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) considers the threshold in absorbed dose for the lens of the eye to be 0.5 Gy, below which tissue reactions(deterministic effects) are unlikely to occur. For other major organs, the thesholds for certain tissue reactions(deterministic effects) are as follows.
| Organs | Effects | One single absorption (Gy) | Prolong absorption (Gy/year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Testes | Temporary sterility | 0.15 | 0.4 |
| Permanent sterility | 3.5 - 6.0 | 2 | |
| Ovary | Sterility | 2.5 - 6.0 | > 0.2 |
| Bone marrow | Depression of hematopoiesis | 0.5 | > 0.4 |
Stochastic effects
The severity of stochastic effects is independent of the absorbed dose. Under certain exposure conditions, the effects may or may not occur. There is no threshold and the probability of having the effects is proportional to the dose absorbed.
Characteristics of stochastic effects:
- Severity is independent of absorbed dose
- Threshold does not exist
- Probability of occurrence depends on absorbed dose
Example: radiation induced cancer, genetic effect
As stochastic effects of radiation have no thresholds and can cause cancers or genetic modifications, of which the curing rates are rather low to date, they become a major subject of research in radiation protection.